Unlocking the Power of SQL Joins:
Your Definitive Guide to Mastery

Table of Contents
Mastering SQL Joins: Understanding the Essence of SQL Joins
Concepts of SQL joins with example with complete guide.
SQL Joins are fundamental in relational databases, enabling the merging of data from multiple tables into a single result set. They allow you to link related data together based on specified conditions, forming a cohesive view of information
A SQL Join statement combines data or rows from two or more tables based on a common field between them. This article gives a brief idea about different types of Joins such as INNER/EQUI JOIN, NATURAL JOIN, CROSS JOIN, SELF JOIN, etc.
Importance of SQL Joins
SQL Joins are foundational to relational databases, enabling data aggregation, relationship establishment, query flexibility, and overall efficient data management, which are integral in various industries and applications.
SQL Joins play a crucial role in database management and querying
Normalization and Database Design :
- Normalization: By distributing data across multiple tables and using joins, databases can be normalized, reducing redundancy and minimizing update anomalies.
- Optimized Database Design: Proper utilization of joins during database design ensures that data is organized efficiently, which is critical for scalability and performance.
Scalability and Performance :
- Optimized Querying: Properly constructed joins and queries contribute to database performance optimization, ensuring faster retrieval times and reduced resource consumption.
- Indexes can be used on joined columns to improve the query performance.
Data Integrity and Accuracy :
- Maintaining Consistency: Joins enforce referential integrity, ensuring that related data remains consistent across tables. This prevents or detects inconsistencies in the database.
Types of SQL Joins with example
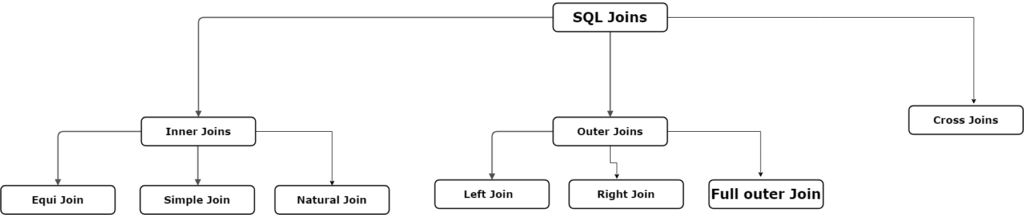
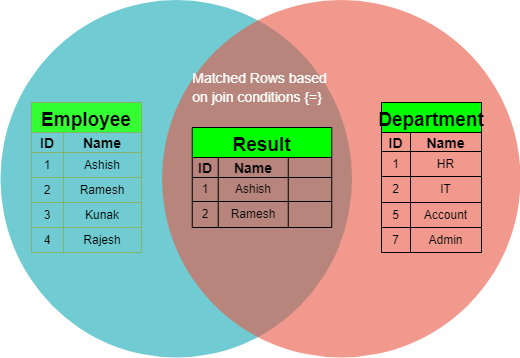
Inner Joins :
Includes joins that retrieve matching records from both tables based on a specified condition.
The SQL inner join combines rows from tables based on fulfilled join conditions [> | < | >= | <= | != | BETWEEN |=]. Illustrated in the following Venn diagram, it retrieves the intersecting rows from both Table X and Table Y
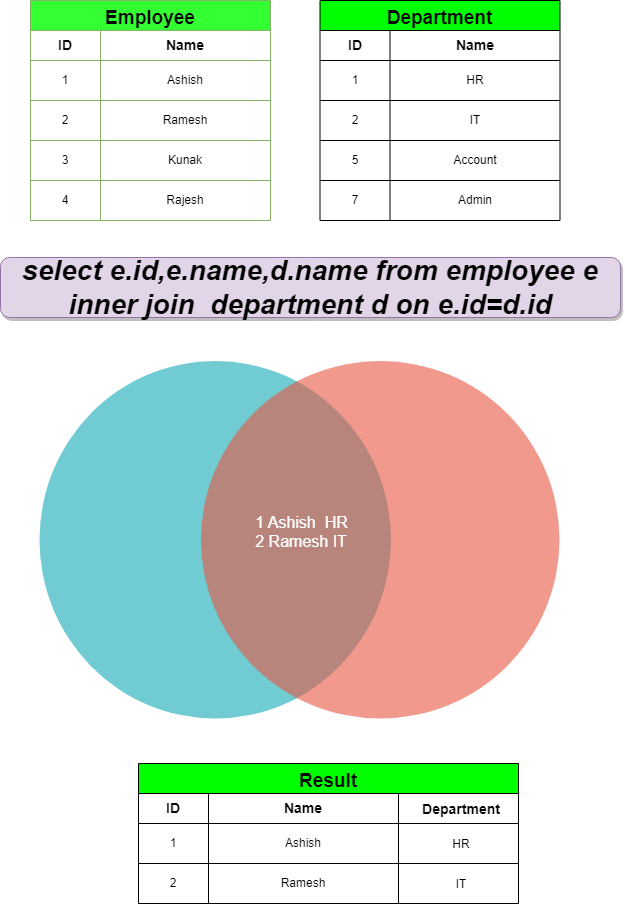
Equi Join :
EQUI Joins, falling under INNER Joins, link two or more tables based on a common column. By employing the equality sign (=), these joins compare data in corresponding columns and fetch matching records.
Types of inner joins that use equality operators (=) to match records.
- Simple Join: Traditional inner join using explicit ‘ON’ clause
- Natural Join: Join that matches columns with the same name in both tables implicitly.
Simple Join :
- Simple Join: Traditional inner join using explicit ‘ON’ clause
Natural Join :
Natural Join: Join that matches columns with the same name in both tables implicitly. Natural Joins merge tables using columns with matching names and identical datatypes. Typically, this join requires a shared attribute (column) between two tables to execute seamlessly3CmxGraphModel%3E%3Croot%3E%3CmxCell%20id%3D%220%22%2F%3E%3CmxCell%20id%3D%221%22%20parent%3D%220%22%2F%3E%3CmxCell%20id%3D%222%22%20value%3D%22select%20e.id%2Ce.name%2Cd.name%20from%20employee%20e%20inner%20join%26amp%3Bnbsp%3B%20department%20d%20on%20e.id%3Dd.id%22%20style%3D%22text%3BstrokeColor%3D%239673a6%3Balign%3Dcenter%3BfillColor%3D%23e1d5e7%3Bhtml%3D1%3BverticalAlign%3Dmiddle%3BwhiteSpace%3Dwrap%3Brounded%3D1%3BfontSize%3D28%3BfontStyle%3D3%3Bshadow%3D1%3B%22%20vertex%3D%221%22%20parent%3D%221%22%3E%3CmxGeometry%20x%3D%22150%22%20y%3D%22-266%22%20width%3D%22620%22%20height%3D%2260%22%20as%3D%22geometry%22%2F%3E%3C%2FmxCell%3E%3C%2Froot%3E%3C%2FmxGraphModel%3E
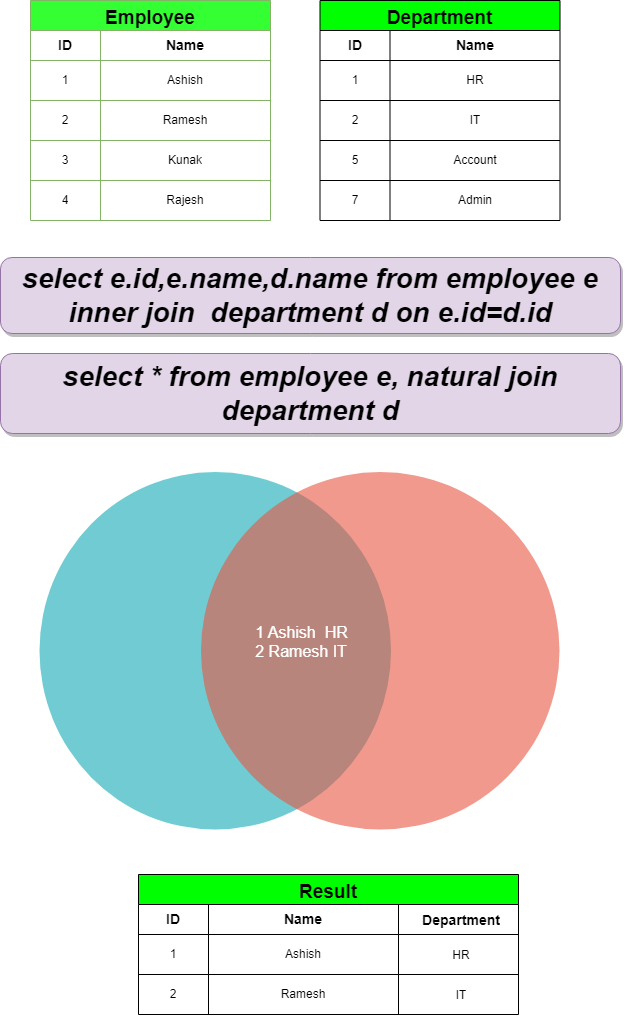
select e.id,e.name,d.name from employee e, department d where e.id=d.id
select * from employee e, natural join department d
Outer Join :
Joins that return matched records and some unmatched records from one or both tables.
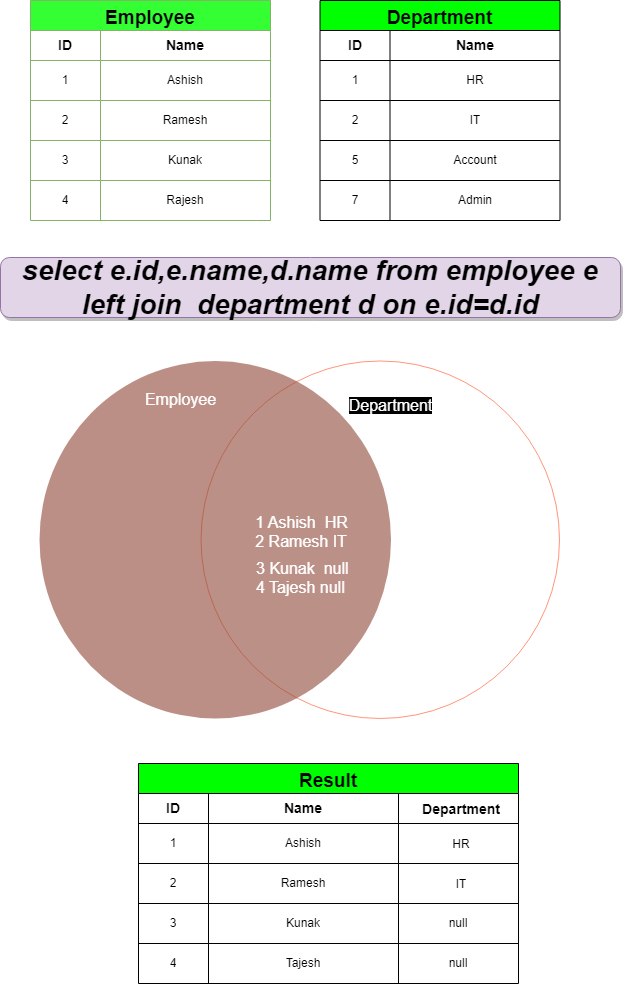
Left Join :
Retrieves all records from the left table and matched records from the right table. There will be no records from right table if no records are matching from Left table
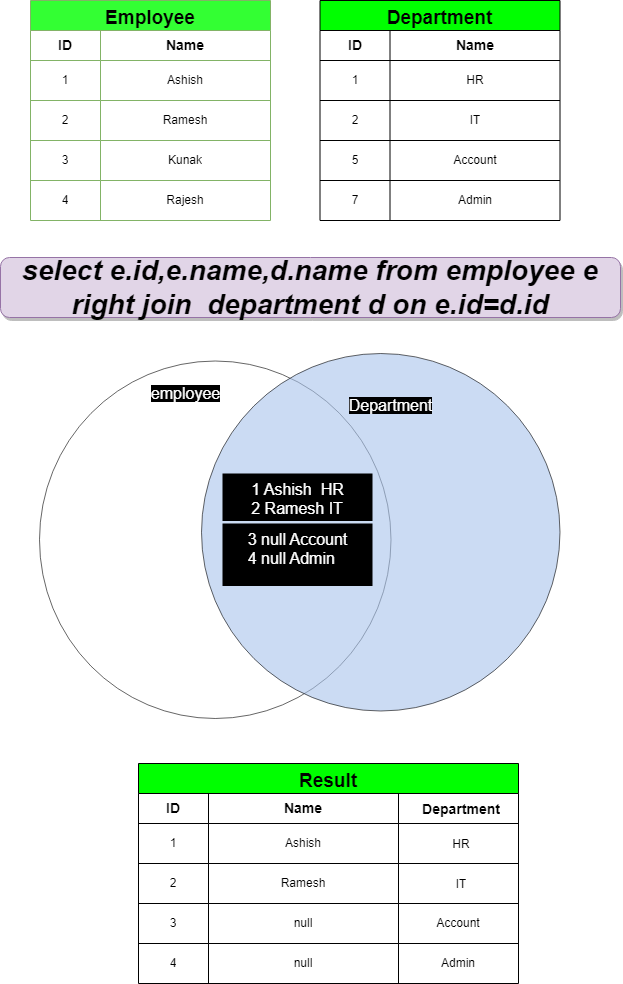
Right Join :
Retrieves all records from the right table and matched records from the left table. There will be no records from left table if no records are matching from righttable
Full Outer Join :
Retrieves all records when there is a match in either the left or right table. Query would return records from both the tables if there are no matching rows result set will return null values.
Cross Join :
A join that produces the Cartesian product of two tables (joins every row from the first table with every row from the second table). This is also called Cartesian join or Cartesian product
Conclusion :
In this Mastering SQL Joins Blog, we have discussed the various type of SQL Join clauses which will help you to streamline data retrieval, and optimize database performance.
So, embrace the learning curve, leverage the diverse join types, and confidently apply these techniques in your projects. With dedication and practice, mastering SQL joins will undoubtedly propel your proficiency in managing data relationships and pave the way for enhanced efficiency and success in your database endeavors
